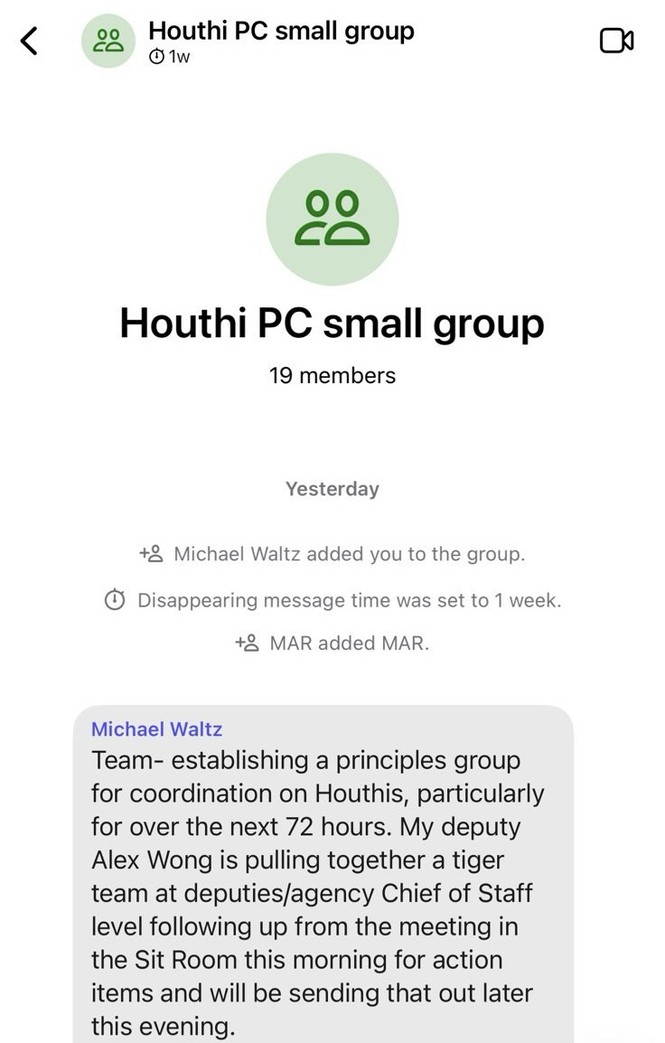
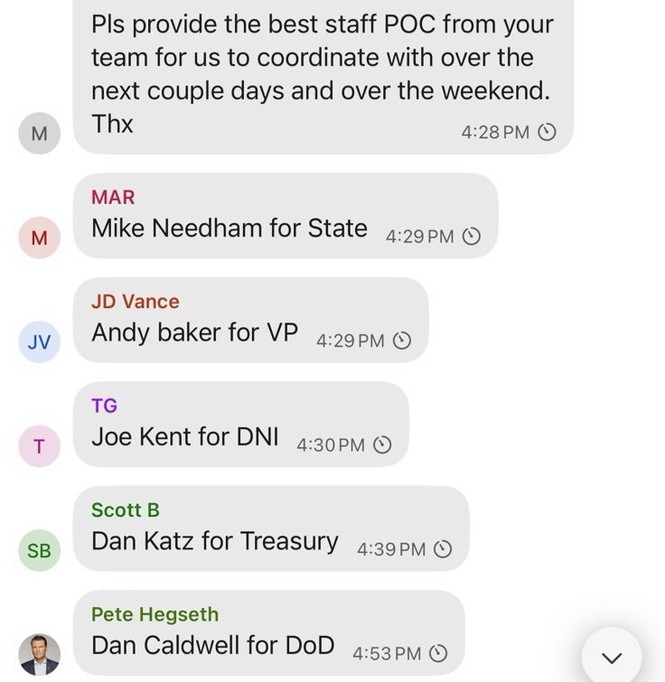
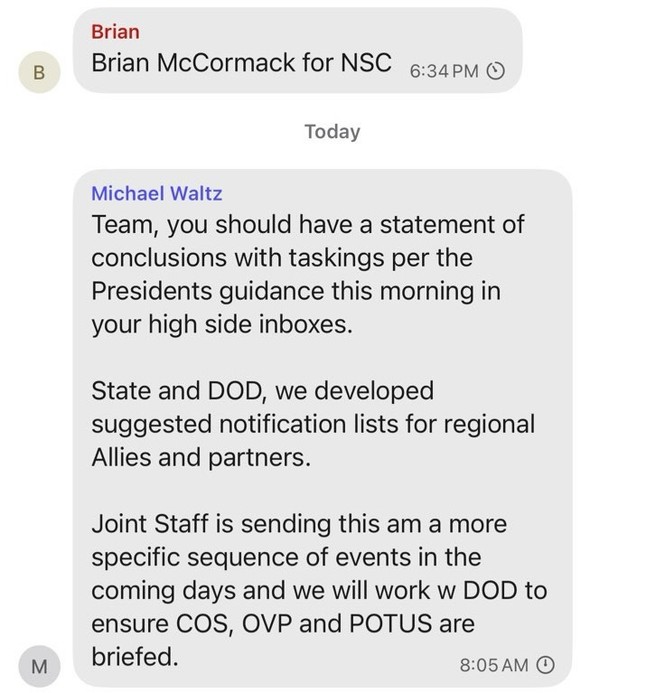
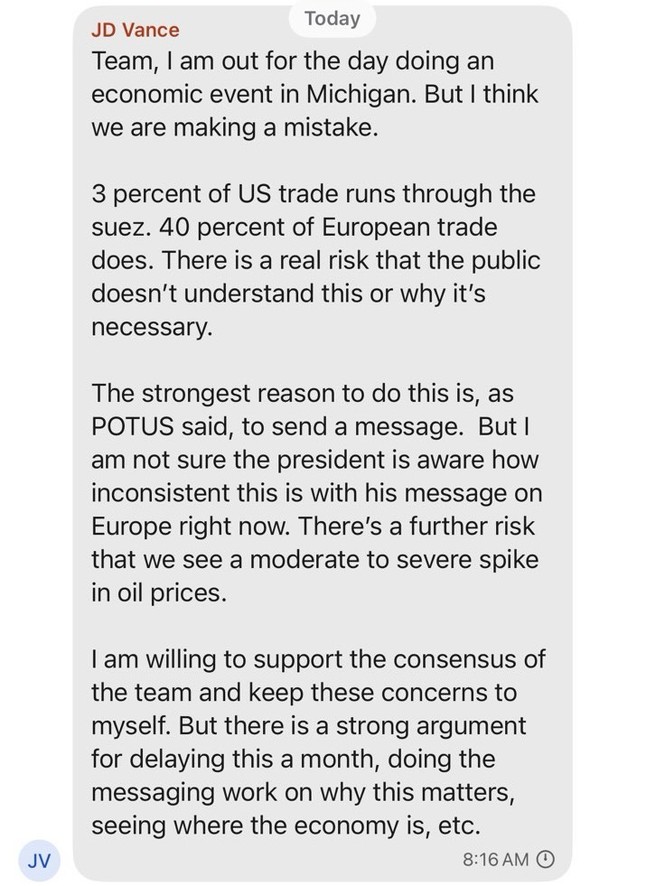
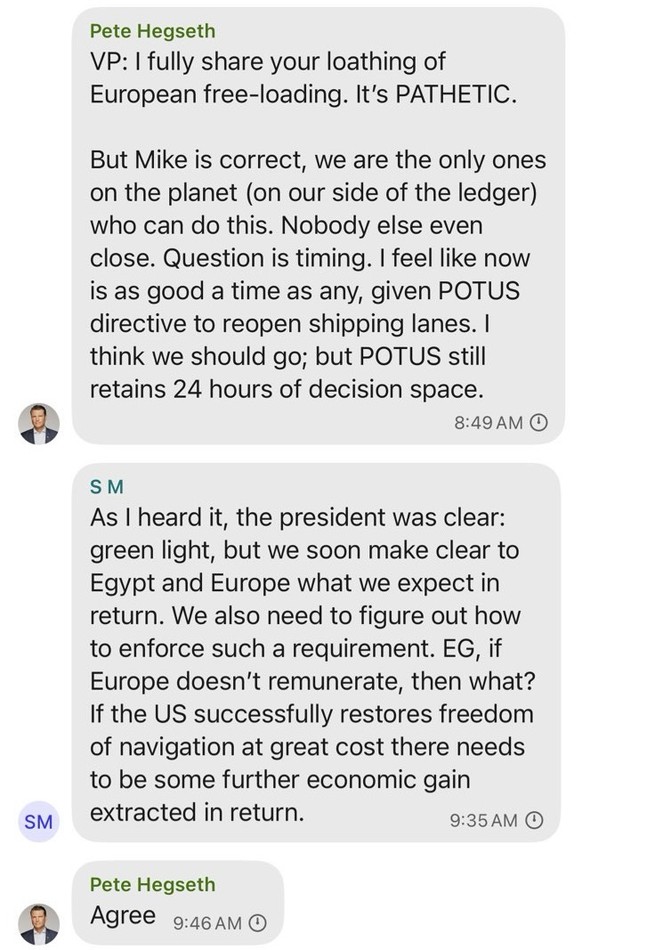
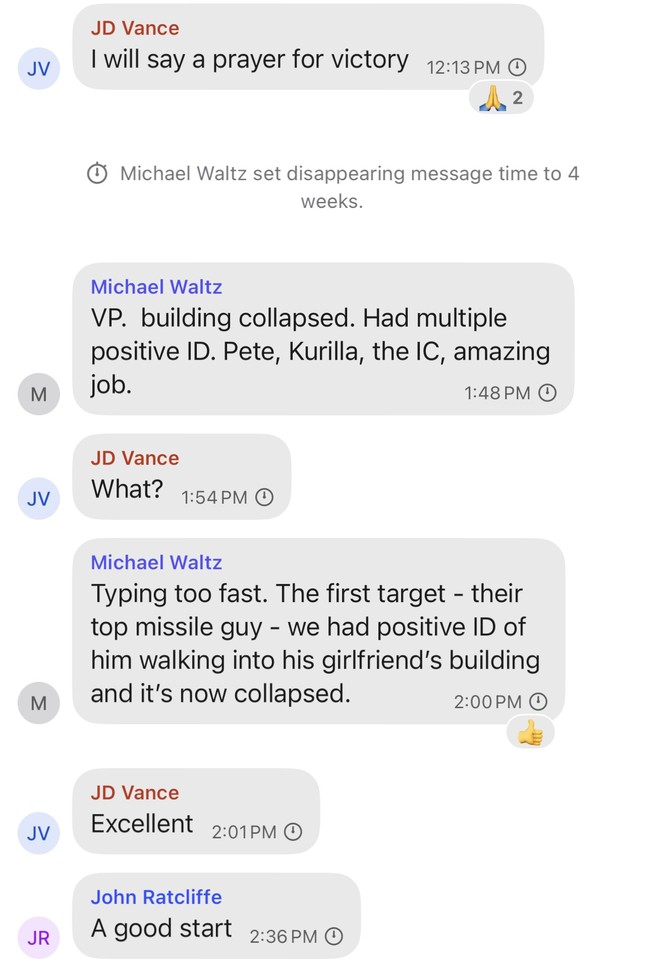
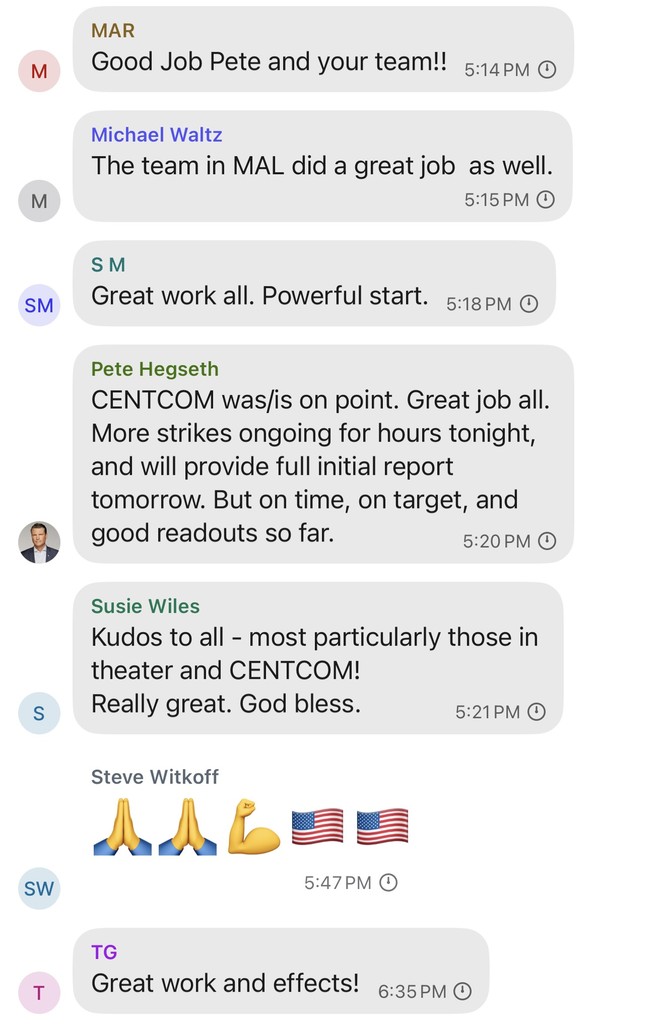
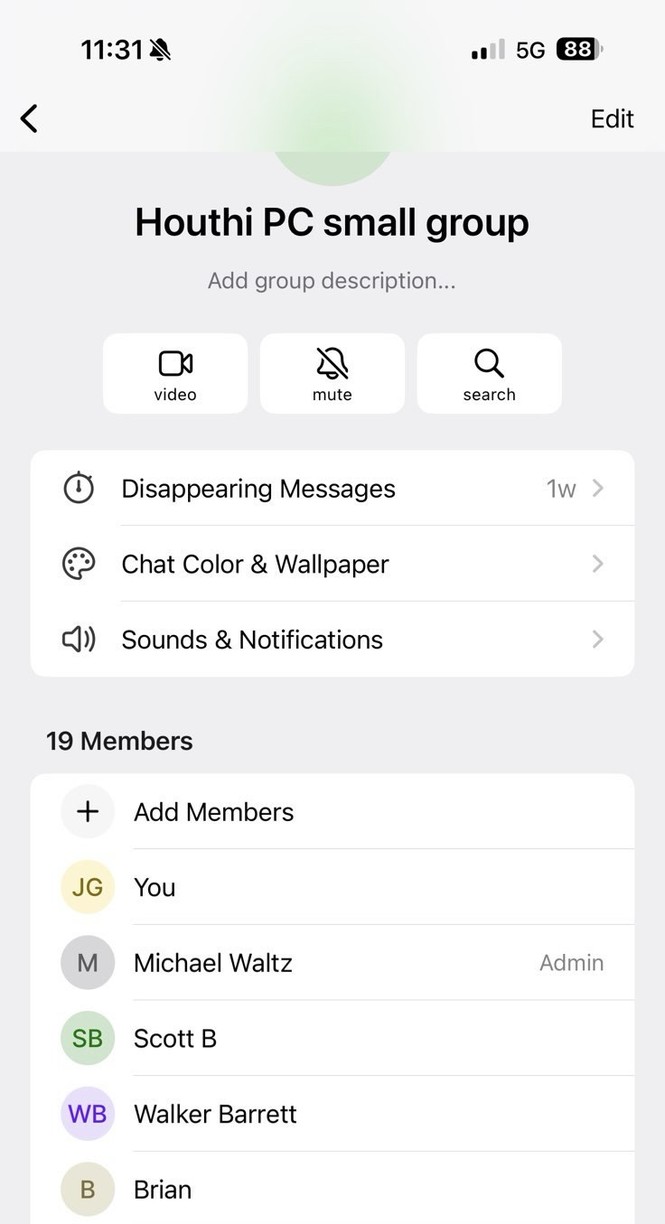
Dana Milbank warns about Trump’s determination to stamp out a free press. The most salient fact about Trump is his narcissism. He demands obeisance, praise, respect, admiration, even groveling. He despises criticism. That’s why he is determined to intimidate journalists and media moguls.
If he can’t intimidate them, he sues them, expecting to intimidate them with financial disaster (he sued CBS for $10 billion for allegedly editing an interview on “60 Minutes”to help Kamala Harris in the election, even though he can’t demonstrate any harm he suffered since he won the election). Milbank does not mention his publisher Jeff Bezos’ obsequious attempts to please Trump by spiking the Washington Post’s editorial endorsement of Kamala Harris and by clamping down on the content of opinion columns, limiting them to praise of “personal liberties” and “free markets.”
The appearance of Milbank’s column is proof that Milbank has not kowtowed to Bezos’ edict, although he does fail to mention that Amazon, also owned by Bezos, paid Melania Trump $40 million to produce a film about her life.
Maybe his last line is a pleas to his boss Bezos, the second richest man in the world.
Milbank writes:
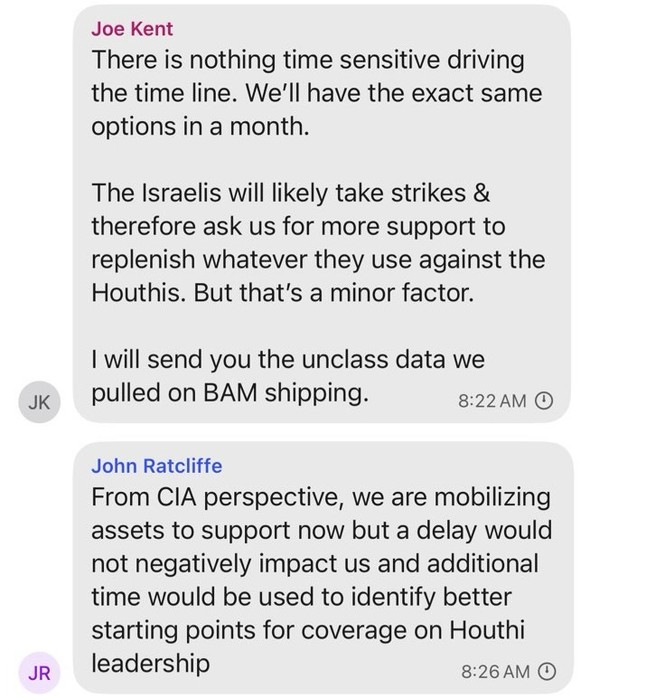
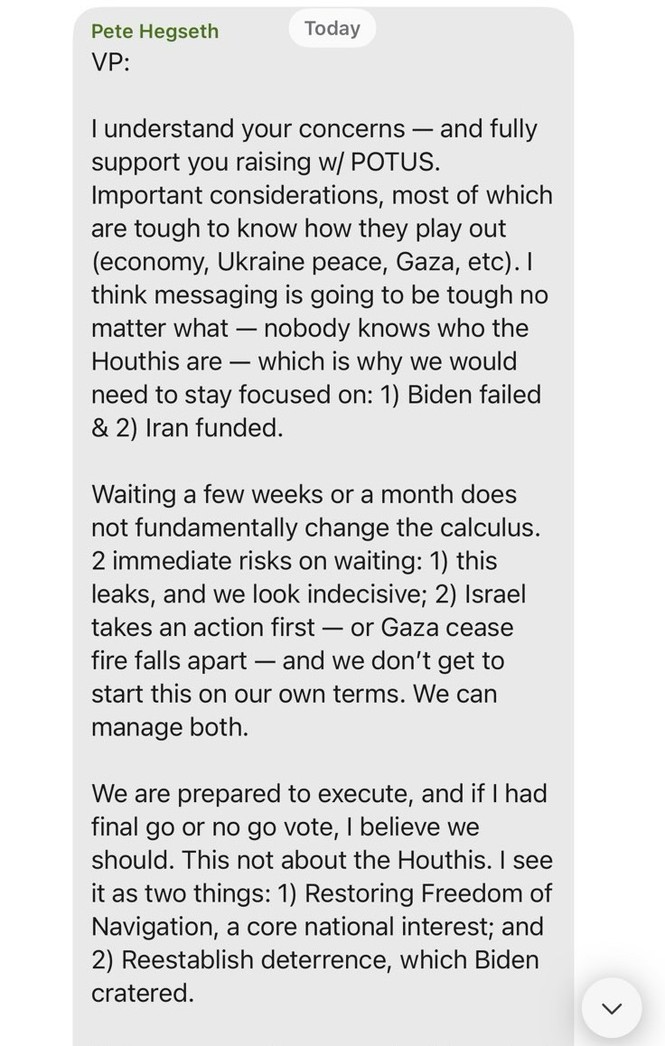
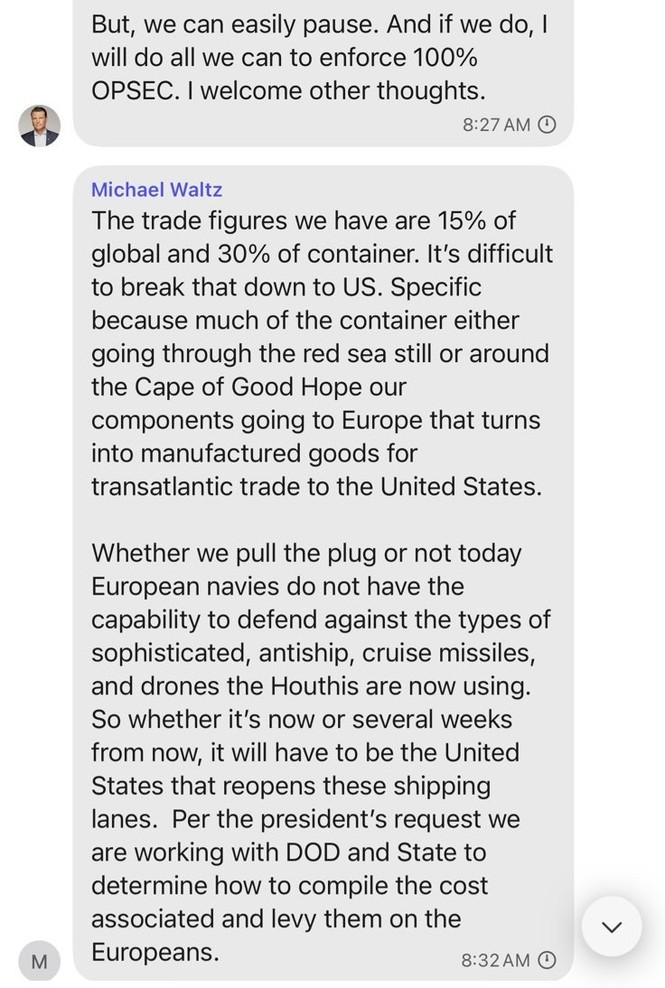
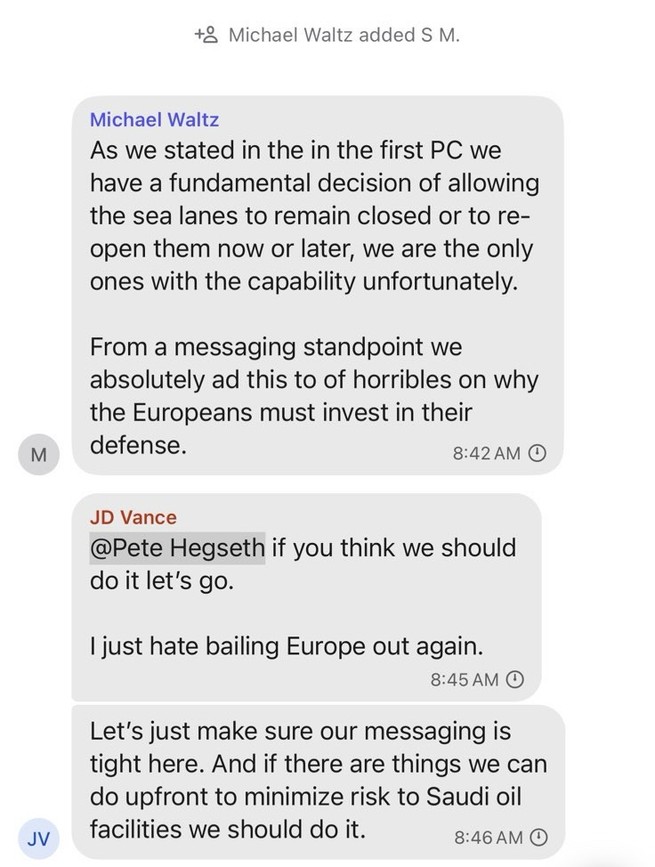
President Donald Trump’s Oval Office ambush of Ukraine’s Volodymyr Zelensky last week was rightly seen as a disaster for freedom in the world. But it also showcased a disaster for freedom at home: the administration’s attempts to extinguish the free press.
Barred by the White House from entering the room that day were the Associated Press and Reuters, venerable news agencies that have covered American presidents for decades. In their place: a correspondent from Russian state media, Tass’s Dmitry Kirsanov. The White House removed Kirsanov from the event in progress, claiming he was not “approved” to be there — asking us to believe that, in an astonishing security lapse, a Russian government propagandist had infiltrated the Oval Office without its knowledge.
Also brought into the room by the White House (which reversed more than a century of practice by seizing from journalists the authority to decide which reporters will be in the press “pool” that has access to Trump): Brian Glenn, correspondent for the MAGA outlet Real America’s Voice and boyfriend of Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-Georgia). He accused Zelensky of “not respecting the office,” asking: “Why don’t you wear a suit?”
Then there was the correspondent from another MAGA outlet, One America News. He told Trump that foreign leaders had “praised your courage and conviction” and asked him “what gave you the moral courage” to start talks with Russian dictator Vladimir Putin about Ukraine, “something that previous leaders lacked the conviction to do.”
“I love this guy,” Trump replied. Upon learning he was from One America News, Trump said: “Well, that’s why I like him. One America News does a great job. That’s very — I like the question. I think it’s a very good question.”
This is the result when the government decides who can cover the president: a sycophantic circus.
The First Amendment tells us that “Congress shall make no law … abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press.”
But Trump tells us otherwise. “Who knows, maybe we will create some NICE NEW LAW!!!” he posted on Truth Social last week, suggesting he wanted to make it illegal for journalists to use anonymous or off-the-record sources, an essential part of newsgathering because it protects people from retaliation. “They are made up, defamatory fiction, and a big price should be paid for this blatant dishonesty,” Trump wrote.
Thomas Jefferson wrote, “Our liberty depends on the freedom of the press, and that cannot be limited without being lost.” But Trump has launched a multipronged attack on our most essential freedom, with precious little pushback:
• His ferociously partisan chairman of the Federal Communications Commission has launched or threatened investigations into ABC, NBC, CBS, PBS, NPR, a website that rates media credibility and radio stations with ties to progressive billionaire George Soros.
• Trump’s acting U.S. attorney for the District of Columbia has threatened to prosecute “anyone who impedes” the work of Elon Musk and his team — a threat widely understood to include journalists.
• Trump himself has kept up a barrage of lawsuits against ABC, CBS, the Des Moines Register (over an inaccurate poll), the Pulitzer Prize board and others, and corporate owners have felt pressured to settle lawsuits they would otherwise win to avoid Trump’s retribution.
• The administration has cut off funds to pro-democracy media outlets in places such as Cuba, Iran and Ukraine, and it is cutting off the editorial independence of Voice of America.
• The president has spread lies about American news organizations, such as Politico and the New York Times receiving USAID funds as a “‘PAYOFF’ FOR CREATING GOOD STORIES ABOUT THE DEMOCRATS” in “THE BIGGEST SCANDAL OF THEM ALL,” and he has ordered government agencies to cancel subscriptions to news outlets.
• Trump on Feb. 23 called NBC and “MSDNC” “an illegal arm of the Democrat Party” that “should be forced to pay vast sums of money for the damage they’ve done to our Country.” He also called for my colleague Eugene Robinson to be “fired immediately” because he didn’t like one of Robinson’s columns that was critical of Republicans.
• Musk last month called for journalists at “60 Minutes” to be given “a long prison sentence” because of their (routine) editing of a Kamala Harris interview during the election. He also said a Wall Street Journal reporter who exposed racist rants by one of Musk’s employees should be “fired immediately.”
• And, of course, there’s the aforementioned White House takeover of the press pool and its banishment of the AP from the Oval Office, Air Force One and similar settings because it still refers to the Gulf of Mexico as the Gulf of Mexico. Trump wants to call it the Gulf of America, but the gulf doesn’t belong exclusively, or even mostly, to the United States, and the rest of the world still uses its traditional name — which is why the AP (and The Post) still uses its traditional name. Posters in the White House briefing room declared “VICTORY” over the AP, which Musk now calls “Associated Propaganda.”
As Rebecca Hamilton, an American University law professor, put it in Just Security last month, it all amounts to “a wholesale effort by Trump and his allies to eviscerate the free press in order to construct an information ecosystem dominated and controlled by those who espouse his views.”
Among Trump’s possible next steps: prosecuting journalists, as some in the administration have threatened. “It is essential that we understand how serious this threat is, because it is much harder to bring things back after they’ve already been finished,” Hamilton tells me. “And so it is worth fighting every single attack on press freedom, even if each attack individually seems like it could be a minor issue.”
The systematic assault on the press is part of a broader crackdown on the civil liberties of those who disagree with Trump. FBI Director Kash Patel has vowed to prosecute Trump’s opponents and critics, and Ed Martin, the D.C. prosecutor, has sent “letters of inquiry” to Rep. Robert Garcia (D-California) and Senate Minority Leader Chuck Schumer, suggesting they were “threatening” Musk (in Garcia’s case) and Supreme Court justices (in Schumer’s case, based on five-year-old remarks he said at the time were not intended as threats). Trump’s border adviser, Tom Homan, has asked the Justice Department to investigate Rep. Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez (D-New York) over her advice to migrants.
More broadly, the administration’s attempts to ban anything that it considers to be “diversity, equity and inclusion” were blocked by a federal judge on First Amendment grounds, because the executive orders force grant recipients to certify that they do not promote DEI. Other agencies have cracked down on expression, including the Pentagon and Veterans Affairs, where the display of gay pride flags has been banned in offices and cubicles.
The efforts are at times clumsy: The day after Wired published an article titled “The Young, Inexperienced Engineers Aiding Elon Musk’s Government Takeover,” Martin sent a public letter to Musk that read like a phishing email from a non-native English speaker. “Anyone imperiling others violating our laws,” proclaimed one sentence in its entirety. “Any threats, confrontations, or other actions in any way that impact their work may break numerous laws,” read another. “We will not act like the previous administration who looked the other way as the Antifa and BLM rioters as well as thugs with guns trashed our capital city. We will protect DOGE and other workers no matter what.”
That’s not the sort of language one typically sees coming from the Justice Department — but these are not normal times. ABC News’s parent company, Disney, paid $15 million to Trump in December to settle a defamation lawsuit — a decision that appeared to be based not on the legal merits but on fear of Trump’s vengeance. Meta in January agreed to pay Trump $25 million to settle a 2021 lawsuit over Trump’s suspended Facebook and Instagram accounts. CBS News parent Paramount Global is now in settlement talks over the “60 Minutes” editing. Even so, FCC Chairman Brendan Carr, a Project 2025 author, joined the attack on CBS, demanding that it hand over the “full, unedited transcript and camera feeds.” Hanging over Paramount if it doesn’t settle Trump’s (frivolous) lawsuit: The FCC could block its planned merger with Skydance.
This is on top of Carr’s probes of NBC parent Comcast (for its supposed DEI practices) and NPR and PBS (for their underwriting practices). Upon arriving, he reinstated complaints of political bias against ABC, CBS and NBC affiliates while declining to reinstate a similar complaint against a Fox affiliate. And he’s probing KCBS radio in San Francisco for its coverage of an immigration enforcement operation. (Not to be outdone, Georgia’s Greene is using her House Oversight subcommittee chairmanship to call the head of NPR to testify about its “blatantly ideological and partisan coverage.”)
Trump’s choice to run Voice of America, failed Arizona gubernatorial and Senate candidate Kari Lake, has vowed to purge the organization of “Trump derangement syndrome.” Last week, VOA suspended veteran journalist Steven Herman over his social media activity, the New York Times reported. A few weeks ago, Trump adviser Richard Grenell called Herman “treasonous” for quoting on social media the president of a democracy advocacy group saying the elimination of the U.S. Agency for International Development “makes Americans less safe at home and abroad.”
The attempted elimination of USAID by the administration has unquestionably hurt efforts to establish a free press in repressive countries. Reporters Without Borders said the sudden freeze of foreign aid programs “has left media organizations around the world in chaos, gravely hampering access to reliable news in zones of serious interest to the United States.” For example, Cubanet, a thorn in the side of Cuba’s regime and an ally of dissidents, was informed that its $1.8 million, three-year grant had been canceled.
So it goes across the Gulf of America, as Trump has decreed it must be called. Unlike, say, restoring the name Mount McKinley in Denali National Park, this is not something Trump can do on his own. Yet the White House said the AP was “lying” by using the name the rest of the world uses. The AP, in its lawsuit seeking reinstatement at the White House, argued that “the Constitution does not allow the government to control speech” and that Americans “have the right to choose their own words and not be retaliated against by the government.” But so far, a judge has rejected the AP’s request.
The gulf tempest may be just an excuse to punish news organizations. The White House is moving to evict some outlets from their seats in the briefing room to make room for MAGA-friendly ones. The Pentagon seized office space that had gone to outlets such as the Times, NPR, NBC and Politico, giving the space to right-wing outlets such as Breitbart, One America News and the New York Post. (It also gave space to liberal HuffPost, which had not requested it.)
This comes on top of the White House’s more egregious move to take control of the press pool, the rotating group of reporters allowed to be in the room with the president. As the White House Correspondents’ Association protested, this means “the government will choose the journalists who cover the president.”
Much of this was proposed in the Project 2025 blueprint, which, despite Trump’s denials during the campaign, has turned out to be a road map for the new administration. It suggested the White House find an “alternative” to the WHCA, take away some of the media’s space in the White House, seize editorial control over VOA and defund public broadcasting, among other things — and variations of all of these policies are underway.
Ominously, Project 2025 also called for rescinding guidance issued by the Biden administration that prevented prosecutors from seizing journalists’ records during leak investigations. The Justice Department “should use all of the tools at its disposal to investigate leaks,” Project 2025 proposed. This, First Amendment advocates fear, implies use of the 1917 Espionage Act to prosecute reporters if they don’t reveal their sources — in effect criminalizing journalism.
Complicating the response by the press to these assaults: Much of American media is owned by corporations and billionaires whose interests are not always aligned with those of a free press. Hamilton, the law professor, calls for “strategic litigation” by media outlets against the administration to push back against the assaults. She says journalists need to “continue to write without self-censoring.” And she says “the public also needs to understand the true value to democracy of having a free press, because if you lose that, then you lose one of the key foundations of accountability in a democracy.”
That’s a lot to ask. But it’s going to take all three — courageous media ownership, fearless journalism and an engaged readership — if the free press is going to survive the Trump presidency.