Fifteen years ago, I wrote a book about the the danger that school choice and testing posed to public schools. Its title: The Death and Life of the Great American School System: How Testing and Choice Are Undermining Education. I named a few of the billionaires funding the attacks on public schools, teachers, and unions–Bill Gates, Eli Broad, and the Walton family–calling them “The Billionaire Boys Club.” Little did I know that they were the tip of the billionaire iceberg.
My hope in 2010 was that public school supporters would block the privatization of their schools. Public schools are as American as apple pie. I wanted the public to wake up, rally around their public schools, and repel the hedge fund managers and billionaires who were funding the privatization movement.
I was too optimistic.
The attacks escalated, fueled by the political power that money buys. The major media bought the corporate reform narrative hook, line, and sinker.
Neoliberal corporate reform brought us high-stakes standardized testing, A-F ratings for schools, charter schools, school closings, and rating teachers by the test scores of their students. And cheating scandals. All to get higher test scores, which never happened.
Now, Jennifer Berkshire asks on her blog The Education Wars whether it’s all over for public schools. Jennifer appreciates the importance of public schools as community builders and civic institutions that serve the common good.
Please read her smart take on the state of public education today:
I won’t lie. If you’re a member of Team Public Education, as I am, it has been a tough summer. And if you, like me, have been sounding the alarm about the dangers of school privatization, it’s impossible to ignore the sense that the future we’ve been warning about has arrived. Five years ago, education historian Jack Schneider and I wrote a book called A Wolf at the Schoolhouse Door: the Dismantling of Public Education and the Future of School that culminated in a sort of “Black Mirror” chapter called “education a la carte.” In it, we described how the ultimate vision of school privatization advocates wasn’t simply to shift the nation’s youngsters into private schools, but to ‘unbundle’ education into a vast array of products for consumers to purchase on Amazon-like exchanges. Lest you think we were exaggerating, turn your attention to Florida, where, as Sue Woltanski documents, project unbundle has arrived with a vengence.
Florida, as usual, is slightly ahead of the curve. But the accelerating collapse of public schools in the state, chronicled in this recent New York Times story, pushed along by the now universal school voucher program, will soon be coming to a state near you. The NYT piece, by the way, was just one of many ‘are public schools over?’ stories to drop in recent weeks. The Washington Post version headed to peer in the window of the GOP vision for education. Spoiler: it entails replacing public schools with “a marketplace of school options.” Then, of course, there was the annual PDK survey of attitudes towards public education, which found both sinking approval of the nation’s schools (with the usual exception for local schools) and rising warmth towards the idea of private school vouchers. As legal scholar Derek Black put it, “The deep well of faith in public education has a disastrous leak.”
To understand what’s happening, I’m going to pause here to spend some time with yet another of the ‘are public schools through?’ stories, Chandler Fritz’s eye-opening new feature for Harper’s, “The Homemade Scholar.” Fritz, a teacher and writer who pens the “Arizona Room” newsletter, took a job at a private religious microschool in order to get a close up view of Arizona’s education marketplace, what he describes as “a new frontier in American education.” I recommend paying attention to this piece because 1) Fritz is a terrific writer and 2) he provides real insights into the appeal of vouchers, or as they’re billed in AZ, education savings accounts—something my own writing rarely reckons with.
Fritz finds a grab bag of reasons that students and parents are drawn to this particular microschool, most of which will be familiar to you: a hunger for ‘customization,’ the desire for religious instruction, the appeal of a small setting, conservative backlash against public education. But there’s another reason we don’t hear as much about—the opposition to the standardized testing that shapes every aspect of what’s left of our public schools. Fritz’s piece is long (the audio version clocks in at nearly an hour), and infuriating in parts, but his observations regarding the attitudes of these ‘education consumers’ towards standardized tests get straight to the point: they hate them.
Bad math
A similar theme pops up in Dana Goldstein’s recent portrayal of the impact of vouchers on schools in Florida’s Orange County. While three quarters of the schools in the district earned an ‘A’ or a ‘B’ on the state’s school accountability report card, parents are eager to free their kids from the burden of taking the state tests, something Florida education watchdog Billy Townsend has been tartly observing for years. Now, I mention opposition to standardized testing here because, even in our deeply divided times, it is a cause that unites parents across virtually any line of division. If you don’t believe me, head down to Texas, where, in addition to re-gerrymandering the state’s electoral maps, legislators have also been pretending to address the popular revolt against the STAAR Test.
But there’s another reason to revisit the antipathy to testing. While you’ve been distracted by the relentless tide of bad and worse news, what’s left of the education reform movement has been busy reemerging, zombie style, seemingly without having learned a single thing about why it flopped in the first place. There are overt signs of the zombie’s return—like Democrats for Education Reform trying to rally the party around a vision of education ‘abundance,’ or Andrew Cuomo, flailing in the NYC mayoral race, now rebranding himself as the education reform candidate with a pledge to shut down failing schools and replace them with new ‘schools of promise.’ Then there’s the pundit-level narrative taking shape in which education reform was working just great until the teachers unions ruined everything and/or Democrats lost their nerve.
This version of events, encapsulated in this recent David Brooks column, goes like this:
School reform was an attempt to disrupt the caste system, to widen opportunity for the less privileged. Presidents Bill Clinton and Barack Obama angered core Democratic constituencies like teachers unions in order to expand opportunity down the income scale. But now Democrats have basically given up. Joe Biden didn’t devote much energy to education reform. Kamala Harris ran for president without anything like a robust education reform agenda.
Brooks goes on to cite Michael Petrilli on the ‘Southern surge,’ the rise in test scores in Mississippi, Alabama, Louisiana and Tennessee (but not Florida) that has education reformers so excited. Kelsey Piper, authoress at the brand new outlet the Argument, is excited too. In her back-and-forth with leftist policy analyst Matt Bruenig over the question of whether giving parents cash benefits poor children, Piper comes down squarely on the side of fixing the schools.
I think school reform after school reform has served every conceivable interest group except students (who do not vote) and so have failed to meaningfully increase literacy and numeracy, even though we now have a road map for how to genuinely let every child thrive.
If you guessed that the ‘road map’ referred to here is Mississippi, you would be correct. Mississippi, by the way, is a national leader in child poverty levels, an honor that the state, which just eliminated its income tax, seems determined to hold on to.
Proxy war
Such ‘if only the band would get back together’ takes somehow miss what a flop much of our recent version of education reform turned out to be. Here’s a partial list. The backlash to Common Core on the right didn’t just help to usher in Donald Trump but played a role in transforming the GOP from the party of big business (which was all in on pushing the Common Core standards) to one dominated by aggrieved populists. And the over selling of college tapped into a well of resentment so deep that the entire system of higher education is now threatened. Then there is the relentless push to narrow the purpose of school down to standardized testing and workforce prep, a bipartisan cause that, as I argue in a forthcoming essay in the Baffler, has now been abandoned by the right in favor of education that prizes ‘virtue’ over vocation, even as many Democrats continue to beat the ‘career readiness’ drum.
I’m not the only one to point this out, by the way. Teacher-turned-writer Nora De La Cour makes a compelling case that the appeal of so-called classical charter schools is due in part to the damage done to public education by neoliberal education reform. Students at these rapidly spreading classical schools encounter the ‘great books.’ Their public school peers get “decontextualized excerpts in corporate-produced test prep materials,” writes De La Cour.
Which brings me to the main point of this piece. (Finally!) Part of what’s so frustrating about our current moment is that by leaning into a deeply unpopular vision for public schools—test them, close them, make them compete—a certain brand of Democrat is essentially incentivizing parents to seek out test-free alternatives. Consider too that we’re in the midst of a fierce intraparty debate over what Democrats need to do to win. For the education reform wing of party, the answer to the question is to go hard at teachers unions and double down on school accountability, while also embracing school vouchers.
While this vision is inherently contradictory, it’s also a loser with voters. There may be no single less appealing sales pitch than ‘we’re going to close your school.’ Just ask former Chicago mayor Rahm Emmanuel, who was so unpopular in the city’s minority neighborhoods after shuttering 50 schools that he couldn’t run for reelection. As voucher programs expand rapidly, we’re about to enter a new era of school closures. If you don’t believe me, just check out this statement from a CATO Institute spox in response to that WaPo story on Arizona:
It’s tough for some families when their school—public or private—closes. Kids miss their friends, teachers worry about their jobs, parents have to adjust their transportation plans. But stories bemoaning public schools losing enrollment due to school choice policies are missing the point. Should parents who want a different option for their children be forced to stay in their assigned school in order to prop it up? Of course not. Public schools had a virtual monopoly on enrollment for decades, but no school can serve the unique needs of all the children who happen to live near it. As we continue down the path of more educational freedom, some schools will rise to the challenge and others will close. We shouldn’t sacrifice children’s futures in an effort to save schools that aren’t meeting their needs.
Close readers will note the moving goal posts—that we’ve moved from school choice as a means of escaping ‘failing schools’ to escaping any kind of school. But the bottom line is that we’re just supposed to accept that ‘education freedom’ means that lots of schools will be closing. Or take the ‘back to the future’ sales pitch for microschools, in which parents “form pods in church basements, barns, and any space they can find. Teachers are launching microschools in their garages.” This vision of what proponents like to call ‘permissionless education’ is one many parents, indeed entire communities, will find difficult to make sense of. It also seems like a gimme for Democrats who are trying to differentiate themselves from the right’s hostility to public schools.
I want to end on a hopeful note, because I’ve depressed us all enough by now, but also because there are some hopeful signs out there. While the education reform zombie may be reemerging, well funded as ever, a growing number of Democrats are showing us what it sounds like to run as an unabashed advocate for public schools. There’s Graham Platner, the challenger to Susan Collins in Maine, who calls out the endless attacks on public schools and teachers as “the tip of the assault on all things public.” Or how about Nathan Sage in Iowa, who puts the defense of public education at the center of his populist platform:
Public schools are the heart of our Democracy, and Republicans are tearing them down brick by brick, while treating our heroic public school teachers like dirt. They are underfunding our public schools and are diverting billions of taxpayer dollars to private schools and into the pockets of billionaires behind them.
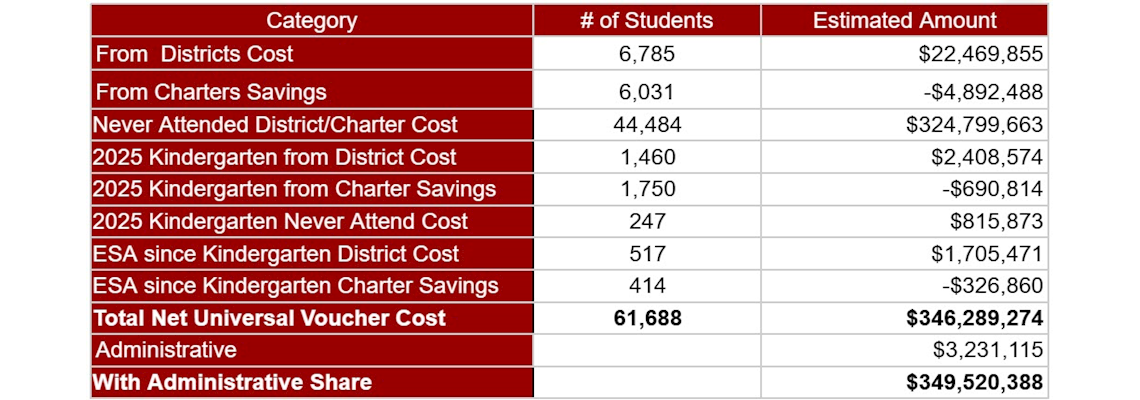
To this list I could add Josh Cowen and Abdul El-Sayed in Michigan, or Catelin Drey in Iowa, who, if she pulls off a win in today’s special election to fill a state senate seat in a district that Trump carried by 11 points, will end the GOP’s supermajority in that chamber. Drey, by the way, is running as a pro-public-education-candidate and an outspoken opponent of Iowa’s controversial universal school voucher program. Plenty of influential Democrats will insist that that message is a loser. That the way for Democrats to win is to run against public schools—to talk about what failures they are, why we need to get tougher on them, and how maybe we don’t actually need them after all. I think they’re wrong, and that voters agree.
Drey did win in Iowa, decisively, proving that a pro-public education stand is a winning message. Drey won 55% of the vote in a district that Trump carried. Her victory broke the Republican supermajority in the state senate.