Michael Hiltzik, the business columnist of the Los Angeles Times, read a recent report by the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget. The report said that Harris’s plans would add $3.5 trillion to the federal debt and Trump’s would add $7.5 trillion. I certainly don’t have the expertise to analyze these numbers, but Hiltzik does. That’s what this column is about. He explains why Trump’s policies would “crater the economy.”
He writes:
If you are wired into the flow of campaign news — as I am, for my sins — you will be inundated this week with reports of a new analysis of the fiscal impact of the economic proposals of Donald Trump and Kamala Harris.
Long story short: Trump’s would be much worse in terms of increasing the federal debt than Harris’. According to the study issued Monday by the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget, Harris’ policies would expand the debt by $3.5 trillion over 10 years, Trump’s by $7.5 trillion.
These are eye-catching figures, to be sure. They’re also completely worthless for assessing the true economic effects of the candidates’ proposals, for several reasons.
One is the committee’s single-minded — indeed, simple-minded — focus on the direct effects of the proposals on the federal deficit and national debt. That’s not surprising, because (as I’ve reported in the past) the CRFB was created to be a deficit scold, funded by the late hedge fund billionaire Peter G. “Pete” Peterson.
For instance, the CRFB has been a consistent voice, as was Peterson, in campaigns to cut Social Security and Medicare benefits on the preposterous grounds that the U.S., the richest country on Earth, can’t afford the expense. (Peterson’s foundation still provides a significant portion of the committee’s budget.)
This focus on the national debt and the federal deficit as a linchpin of economic policy dates back to the 1940s among Republicans and the 1970s among Democrats. Throughout that period it made policymaking more austere and left the country without the resources to address real economic needs such as poverty while increasing inequality.
The harvest, as economist Brad DeLong of UC Berkeley has noted, was the rise of a policy that failed everyone but the rich. Trump would continue that policy; Harris would continue the Biden administration’s effort to return the U.S. to a government that serves all the people.
The worst shortcoming of the CRFB’s analysis is that it’s hopelessly narrow. Its focus is on the first-order effects of the individual proposals on federal income and spending, without paying much attention to the dynamic economic effects of those policies. Would the policy spur more growth over time, or less?
Another problem with the analysis is that the candidates’ proposals are inchoate — as the committee acknowledges. The committee cobbled together their purported platforms from written policy statements, social media posts and dubious other sources and then absurdly claimed that its effort helped to “clarify [the] policy details.”
The committee estimates the direct cost of Harris’ proposal to extend and increase the health insurance subsidies created by the Affordable Care Act and improved by the Biden administration at $350 billion to $600 billion over 10 years; but what would be the gains in gross domestic product from reducing the cost of healthcare for the average household?
The committee barely even acknowledges that this is a salient issue. It says that in some of its estimates it accounts for “dynamic feedback effects on revenue and spending,” but also says, “we do not account for possible changes in GDP resulting from the candidates’ policies.”
The committee’s treatment of Trump’s tariff proposals demonstrate the vacuum at the heart of its analysis. It treats the income from Trump’s proposal — a 10% to 20% tariff on most imported goods and 60% on Chinese imports — as a revenue gain for the federal budget. Economists are all but unanimous in regarding tariffs as a tax on American consumers, however — in other words, a tax transferring household income to the Treasury.
The committee writes: “Such a significant change to trade policy could have economic and geopolitical repercussions that go beyond what a standard tax model would estimate.” As a result, “the true economic impact is hard to predict.” Thanks for nothing.
Uncertainties about the details of the candidates’ proposals resulted in laughably wide ranges in the committee’s fiscal estimates. The effect on the deficit and debt of Harris’ proposals is estimated at zero to $8.1 trillion over 10 years. For Trump’s plans, the range is $1.45 trillion to $15.15 trillion. What are voters or policymakers supposed to do with those figures?
The CRFB also reports a “central” estimate for both — $3.5-trillion expansion of debt for Harris, $7.5 trillion for Trump — but doesn’t say much about how it arrived at those figures, other than to say that sometimes it just split the difference between the high and low estimates, and sometimes relied on estimates of the individual proposals by the Congressional Budget Office and the congressional Joint Committee on Taxation.
I asked the CRFB to comment on the shortcomings listed above, but haven’t received a response.
Despite all that, the CRFB analysis showed up on the morning web pages of major newspapers and other media coast to coast on Monday, as though its conclusions were credible, solid and bankable. (Here at The Times, we passed.)
Consider the CRFB’s treatment of Trump’s deportation policy, which he has called the “largest deportation program in American history,” affecting at least 11 million undocumented immigrants and millions more who are in the U.S. legally.
The committee says that might increase the deficit by anywhere from zero to $1 trillion over a decade, with a middle-of-the-road estimate of $350 billion — “chiefly,” it said, “by reducing the number of people paying federal taxes.” It also cites unspecified “additional economic effects of immigration.”
The CRFB might have profited from reading an analysis of the deportation proposal produced in March by the Peterson Institute for International Economics, which was also funded by Pete Peterson but, staffed by economic eggheads with a wider intellectual horizon, tends to take a more intelligent approach to economic policy.
“The immigrants being targeted for removal are the lifeblood of several parts of the US economy,” the institute observed. “Their deportation will … prompt US business owners to cut back or start fewer new businesses, … while scaling back production to reflect the loss of consumers for their goods.”
The institute cited estimates that a deportation program in effect from 2008 to 2014 cost the jobs of 88,000 U.S. native workers for every 1 million unauthorized immigrant workers deported. Arithmetic tells us that, in those terms, deporting 11 million immigrants would cost the jobs of about 968,000 U.S. natives.
“The disappearance of migrant workers … dries up local demand at grocery stores, leasing offices, and other nontraded services,” the institute reported. “The resulting blow to demand for all workers overwhelms the reduction in supply of foreign workers.”
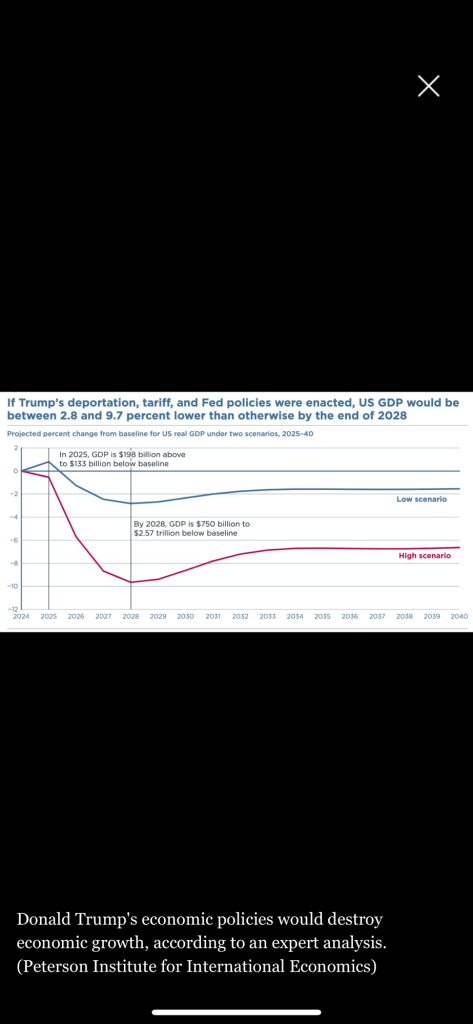
The institute was a lot more free-spoken than the CRFB about the effect of Trump’s proposed policies on economic growth. Considering only the deportations, tariffs and Trump’s desire to exercise more control over the Federal Reserve System, it concluded that by the end of Trump’s term, U.S. GDP would be as much as 9.7% lower than otherwise, employment would fall by as much as 9%, and inflation would climb by as much as 7.4 percentage points.
An overly sedulous focus on deficit reduction as economic policy has caused “real harm [for] the nation’s most vulnerable groups, including millions of debt-saddled and downwardly mobile Americans,” economic historian David Stein of the Roosevelt Institute and UC Santa Barbara wrote last month. When it became Democratic orthodoxy under Presidents Carter and Clinton, the party pivoted to “‘Reagan Democrats’ and suburban white voters at the expense of the labor and civil rights movements.”
As the federal government pulled back, “state budgets were ravaged,” Stein wrote. State and local services were slashed. The efforts to control federal debt forced households to take on more debt.
The deficit scolds are still at it and still have vastly more credibility than they deserve. That’s clear from the CRFB’s analysis and the alacrity with which it was republished as “news” Monday. Efforts to turn policy back to the point that it benefits everyone, not just the rich, still have a long way to go in this country.

